-
[Java_Basic]클래스의 상속1 : 상속의 기본(윤성우의 열혈 Java 프로그래밍)Java/Basic 2021. 1. 2. 13:49
상속
연관된 일련의 클래스들에 대해 공통적인 규약을 정의할 수 있다
(단순히 재활용의 목적으로 상족이 쓰일 경우 무의미한 코드가 될 수 있다)
상속의 특성
부모 클래스
class Man{ String name; public void tellYourName(){ System.out.println("My name is " + name); } }자식클래스
class BusinessMan extends Man{ //Man 클래스를 상속하는 클래스 String company; String position; public void tellYourInfo(){ System.out.println("My company is" + company); System.out.println("My position is " + position); tellYourName(); //Man 클래스를 상속했기 때문에 호출 가능 } }BusinessMan man = new BusinessMan();
해당 참조변수 man이 사용 가능한 인스턴스들
String name;
String company;
String position;
void tellYourName(){...}
void tellYourInfo(){...}
상속과 생성자
class Man{ String name; public void tellYourName(){ System.out.println("My name is " + name); } } class BusinessMan extends Man{ String company; String position; public BusinessMan(String name, String company, String position){ //상위클래스 Man의 멤버 초기화 this.name = name; //클래스 BusinessMan 의 멤버 초기화 this.company = company; this.position = position; } public void tellYourInfo(){ System.out.println("My company is " + company); System.out.println("My position is " + position); tellYourName(); } } class MyBusinessMan{ public static void main(String[] args){ BusinessMan man = new BusinessMan("YOON", "SAMSUNG", "CEO"); man.tellYourInfo(); } }
이렇게 부모 클래스의 변수도 자식 클래스에서 초기화해주면 에러는 발생하지 않지만 이건 좋은 방법이 아니다.
모든 멤버는 그 멤버가 생성된 클래스 안에서 초기화 하는것이 좋다.
class SuperCLS{ public SuperCLS(){ //생성자 System.out.println("I'm Super Class"); } } class SubCLS extends SuperCLS{ public SubCLS(){ //생성자 System.out.println("I'm Sub Class"); } } class SuperSubCon{ public static void main(String[] args){ new SubCLS(); } }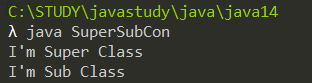
해당 결과를 보니 하위 클래스의 인스턴스 생성 시 상위 클래스, 하위클래스의 생성자가 모두 호출됨을 알 수 있다.
또한 하위클래스의 인스턴스 생성시 상위 클래스의 생성자가 먼저 호출이 된다.
이로써 하위 클래스에서 상위 클래스의 생성자를 명시적으로 호출하지 않으면 인자를 받지 않은 생성자가 자동으로 생성됨을 알 수 있다.
상위 클래스의 생성자를 명시적으로 호출하기 위해 키워드 super를 사용한다.
키워드 super
class SuperCLS{ public SuperCLS(){ System.out.println("Con : SuperCLS()"); } public SuperCLS(int i){ System.out.println("Con : SuperCLS(int i)"); } public SuperCLS(int i, int j){ System.out.println("Con : SuperCLS(int i, int j)"); } } class SubCLS extends SuperCLS{ public SubCLS(){ System.out.println("Con : SubCLS()"); } public SubCLS(int i){ super(i); //상위 클래스의 생성자를 지정 및 호출 System.out.println("Con : SubCLS(int i)"); } public SubCLS(int i, int j){ super(i, j); //상위 클래스의 생성자 지정 및 호출 System.out.println("Con : SubCLS(int i, int j)"); } } class SuperSubCon2{ public static void main(String[] args){ System.out.println("1. "); new SubCLS(); System.out.println(); System.out.println("2. "); new SubCLS(1); System.out.println(); System.out.println("3. "); new SubCLS(1,2); System.out.println(); } }
class Man{ String name; public Man(String name){ this.name = name; } public void tellYourName(){ System.out.println("My name is " + name); } } class BusinessMan extends Man{ String company; String position; public BusinessMan(String name, String company, String position){ super(name); this.company = company; this.position = position; } public void tellYourInfo(){ System.out.println("My company is " + company); System.out.println("My position is " + position); tellYourName(); } } class MyBusinessMan2{ public static void main(String[] args){ BusinessMan man = new BusinessMan("YOON", "SAMSUNG","CEO"); man.tellYourInfo(); } }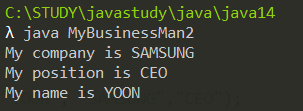
static 상속
static 선언이 붙는 클래스 변수와 클래스 메소드는 상속의 대상이 아니다.
직접 접근하는 권한은 자식도 갖게 된다.
class SuperCLS{ static int count = 0; public SuperCLS(){ count++ } }class SubSLC extends SuperCLS{ public void showCount(){ System.out.println(count); } }protected 는 하위 클래스 접근을 허용한다.
private 되면 접근 불가이다.
class SuperCLS{ protected static int count = 0; public SuperCLS(){ count++; } } class SubCLS extends SuperCLS{ public void showCount(){ //상위 클래시에 위치한 클래스 변수 count 에 접근 System.out.println(count); } } class SuperSubStatic{ public static void main(String[] args){ SuperCLS obj1 = new SuperCLS(); //count 값 1 증가 SuperCLS obj2 = new SuperCLS(); //count 값 1 증가 // 아래 인스턴스 생성 과정에서 SuperCLS 생성자 호출 되므로, SubCLS obj3 = new SubCLS(); //count 값 1 증가 obj3.showCount(); } }'Java > Basic' 카테고리의 다른 글
[Java_Basic]클래스의 상속3 : 상속의 목적(윤성우의 열혈 Java 프로그래밍) (0) 2021.01.02 [Java_Basic]클래스의 상속 2 : 오버라이딩(윤성우의 열혈 Java 프로그래밍) (0) 2021.01.02 [Java_Basic]배열(윤성우의 열혈 Java 프로그래밍) (0) 2021.01.02 [Java_Basic]콘솔 입력과 출력(윤성우의 열혈 Java 프로그래밍) (0) 2021.01.02 [Java_Basic]메소드의 오버로딩과 String 클래스(윤성우의 열혈 Java 프로그래밍) (0) 2021.01.02